Which of the Following Is True of Control Charts
Control charts are statistical tool showing whether a process is in control or not. Identify the special cause and address the issue.
Senior management and project managers.

. As the sigma level for a control chart increases the likelihood of concluding the process is out of control when in reality it is in control decreases. Which of the following is true about using control charts to monitor process performance to ensure quality. Trend type of control chart pattern shows continuous movement of points upwards and downwards 2.
Conventional statistical process control charts have the lowest frequency of false alarms. At a factory a lag in testing could mean that thousands of parts are produced incorrectly before anyone notices the machine is broken. The second referred to asa multivariate control chart is a graphical display of a statisticthat summarizes or represents more than onequalitycharacteristic.
Just remember it is three sigma limits of what is being plotted. This shows process capability and helps you monitor a process to see if it is within acceptable parameters or not. Fraction of nonconforming units 2.
There are multiple kinds of control charts. Quality is now an integral part of strategic planning. The P-chart is also known as the fraction defectives or fraction non-conforming chart because it is used to monitor and control the fraction produced in a process that is defective or non-conforming.
The descriptions below provide an overview of the different types of control charts to help practitioners identify the best chart for. Characteristics of control charts. For the Control Chart tool students select a mean and standard deviation for the process from when the process is in control and then decide on a sample size.
The X bar chart control limits are derived from the R bar average range values if the values are out of control in R chart that means the X bar chart control limits are not accurate. A II and III only are true. Specification limits are the same as control limits.
B I and II only are true. X bar and R Chart X bar and sigma chart the chart for the individual units. A shift in the average will show up on the X portion of the X and R chart.
Remove those subgroups from the calculations. If the process is in control half the points will fall below the center line. Trend pattern occurs due to change in inspection method 3.
Control charts alone can determine the source of problems. The use of small sample sizes in control charts increases the chances that a process may have changed during the sampling interval. A control chart illustrates process behaviors by detecting changes in a process.
If the process is in control 2700 points per million will fall outside the control limits. Conventional statistical process control charts have the lowest frequency of false alarms. Downward trend indicates wear of parts.
Which of the following is true of control charts. If there is no assignable cause of variation the process is in control. Standard control charts are not effective when the rate of defects is extremely low.
Control charts can only be used for processes that have a very high sigma level. Number of nonconforming units 3. Control charts have upper and lower limits that indicate the range of acceptable values.
Control charts for the variable type of data X bar and R charts. Control charts have two general uses in an improvement project. A company dedicated to quality usually provides training for.
If you are plotting individual values eg the X control chart for the individuals control chart the control limits are given by. In industrial settings control charts are designed for speed. If a single quality characteristic has been measured or computedfrom a sample.
Quality is defined by the customer. These lines are determined from historical data. Standard control charts are not effective when the rate of defects is extremely low.
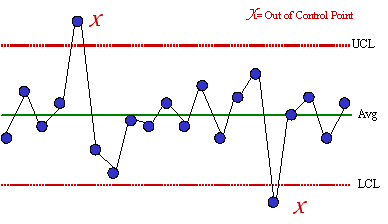
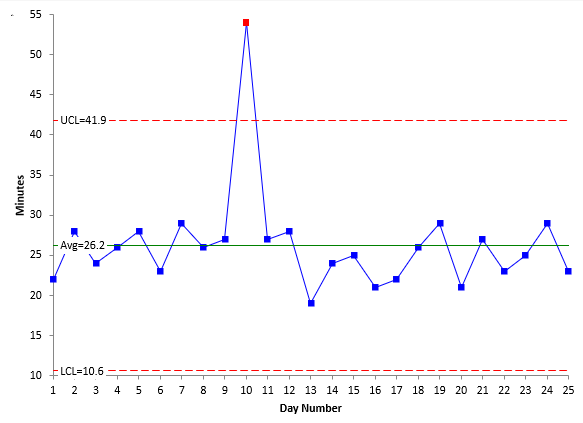
The X- Bar chart monitors process upper limit conformance. A control chart always has a central line for the average an upper line for the upper control limit and a lower line for the lower control limit. Standard control charts are not effective when the rate of defects is extremely low.
Which of the following statements are true regarding control charts. Control limit equations are based on three sigma limits. The use of small sample sizes in control charts increases the chances that a process may have changed during the sampling interval.
Which of the following is true about control charts. The width of the limits is inversely proportional to the square root of the sample size. A process should be halted and investigated if the sample result is between the upper control limit and the lower control limit.
Control charts tell the operator when to do something and when to do nothing. Four widely-used attributes control charts are. Data points above the upper control limits mean that the products quality is beyond expectations.
The most common application is as a tool to monitor process stability and control. The process is under control if the same observations form a. The faster the control charts respond following a process shift the faster the engineers can identify the broken machine and return the system back to producing high-quality products.
A less common although some might argue more powerful use of control charts is as an analysis tool. The control chart includes everything a run chart does but adds upper control limits and lower control limits at a distance of 3 Standard Deviations away from the process mean. If the points are out of control in R chart then stop the process.
After students have determined and entered correct values for the upper and lower control limits the Control Chart tool will draw the reference lines on the control chart. Total number of nonconformities per unit 4. Control charts can be used to monitor a process for the existence of special cause variation.
So what does that mean. Which of the following is true of control charts. All of the above statements are true.
The first referred to as aunivariate control chart is a graphical display chart ofonequality characteristic. Attribute charts are meant for attribute type of data. By comparing current data to these lines you can draw conclusions about whether the process variation is consistent in control or is unpredictable out of control affected by special.
P chart np chart c chart u chart U chart. Two types of process data. Quality has become a competitive weapon.
UCL AverageX 3SigmaX LCL AverageX - 3SigmaX. Control charts have a center line that represents an average of the process. As the sigma level for a control chart increases the likelihood of concluding the process is out of control when in reality it is in control increases b.
Variable is a continuous data things we can. Control chart is a real-time time-ordered graphical process feedback tool designed to tell an operator when significant changes have occurred in the manufacturing process. The major components of a control chart are the lower control limits the center line and the upper control limits.
Types of Control Charts. Which of the following statements isare true. The use of small sample sizes in control charts increases the chances that a process may have changed during.
Conventional statistical process control charts have the lowest frequency of false. Variable charts are meant for the variable type of data. Average number of nonconformities per unit 71 The p-chart and np-chart with Equal Sample Sizes 711 p-chart for Known or Speci ed p.

Solved Question 2 Which Of The Following Statements Are True Chegg Com

Statistical Process Control Product Process Improvement Presentationeze Process Control Statistical Process Control Statistical
No comments for "Which of the Following Is True of Control Charts"
Post a Comment